This post began as a joyful moment I shared online: a video of James and I signing in Makaton at Heathrow, with a caption that read:
“The world is changing in a magnificent way. We didn’t have these self-service wheelchairs in December, and now we do! The stress relief and anxiety reduction is immense. Happiness is peace, understanding, accommodation and acceptance.”
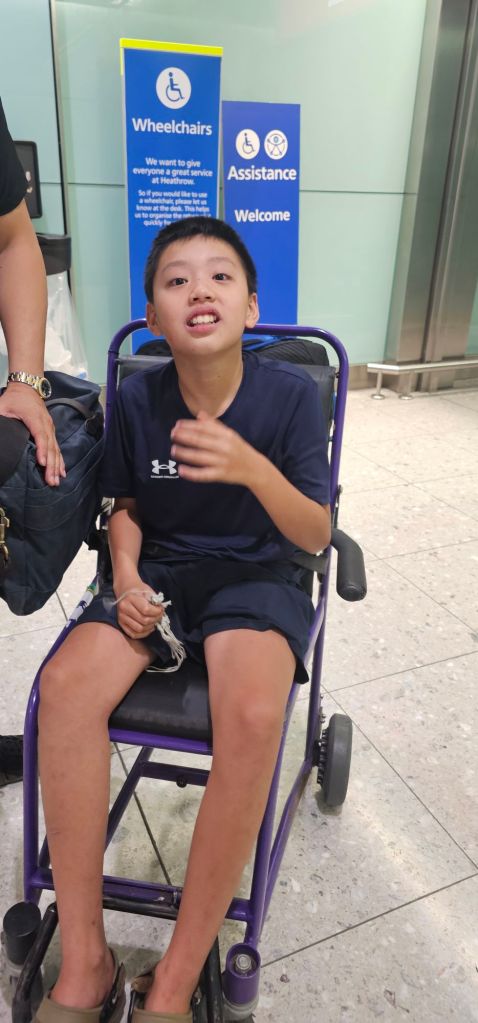
That change—wheelchairs available to borrow like luggage trolleys—sparked another thought.
When are we enabling agency, and when are we quietly reinforcing exclusion?
We’ve seen similar setups in supermarkets lately, the choice to help yourself without a lengthy registration process. It’s a small but powerful step toward everyday inclusion.
This was our first time using this service. Although I don’t plan to do it often or take advantage of it, I was grateful it was there. I want to encourage James to adapt when he can. But sometimes, circumstances dictate. And this time, it was the safer, easier, and kinder choice for both of us.
Still, I wondered if people were confused—seeing James in a wheelchair when he’s perfectly capable of walking. To be honest, I didn’t have time to worry about what others thought. He managed to dash off anyway. Specifically, he eloped.
Elopement
Eloping is the SEND (Special Educational Needs and Disabilities) term for this sudden, fast, unplanned running off. It’s a type of fight-or-flight behaviour often seen in autistic children, especially those with intellectual or learning disabilities.
Eloping, in the context of children with special needs, evokes a deep, instinctual panic. It is the kind that freezes your heart. It turns your stomach to stone. It happens in seconds. Your child slips from your grasp and bolts.
It’s not misbehaviour. It’s communication. Or it’s overload. Or it’s fear. Or sometimes, it’s just the only response a child has. We’ve experienced elopement in shopping centres, schools, restaurants, playgrounds. It’s scary. Avoiding these places altogether isn’t sustainable—or healthy. So we build a toolkit, and we remain alert.
Parenting or supporting a non-speaking autistic child with learning disabilities requires constant micro-decisions that are both ethical and practical. Each decision sits within a continuum:
- Support vs. over-support
- Protecting safety vs. restricting autonomy
- Reducing demands vs. reducing opportunity
- Adapting the world vs. unintentionally narrowing it
In this sense, inclusion is an ongoing negotiation. Families must continually evaluate the line between enabling agency and reinforcing passive dependence — a line that is influenced by risk, resources, social expectations, and their own emotional capacity.
Our airport ‘toolkit’
We don’t usually book special assistance services at airports, but we do carry a doctor’s letter explaining James’s needs. We book night flights. We pack familiar snacks and toys, print airport pictures in advance, and bring sensory items. Sometimes, I take anti-anxiety medication, not just for myself, but to ensure my fear doesn’t amplify his. That’s the hidden layer behind invisible disabilities and “He looks fine.”
Neurodiversity: Seeing the Bigger Picture
I sometimes prefer to talk about neurodiversity through characteristics rather than diagnostic criteria. From my own experience, I’ve found that the “defining characteristics” of autism have sometimes overshadowed James’s other learning needs—especially speech and language delay, apraxia, and global developmental delay.
Invisible or unseen can mean we often don’t know the full extent or cause—and we certainly can’t measure potential based on what we know so far.
The Unseen Population
There is a whole group of children and young people who rarely make it into the centre of conversations about autism, learning disability, or inclusion — not because they are small in number, but because they are harder for the world to see.
Children who don’t speak. Children without a reliable communication system. Children whose bodies don’t move the way they want them to.
In classrooms, they are sometimes placed in the corner with good intentions, but low expectations. In society, they are praised when compliant, overlooked when curious, and misunderstood when distressed. None of these are the failures of the child. They are failures of our society and system.
There is still so little research into children without speech or formal communication. This population—those with the most complex disabilities—are often overlooked, omitted, or researched upon rather than with. They become theory, not fully recognised and respected lives.
Presuming competence sounds simple on paper.
But in the real world, it bends and blurs.
Capacity rises and falls with noise, hunger, fear, fatigue, environment, chemistry, chance.
Some days we stretch the world to meet our children.
Some days we shrink their world to keep them safe. When are we nurturing agency — and when, without meaning to, are we teaching helplessness?
When are we opening doors — and when are we simply decorating the walls of a small room?
There is no universally “correct” position because every child and context is different. However, the critical question remains:
Are we creating conditions that allow the child to be an active participant in their life, or are we — intentionally or not — positioning them as passive recipients of care?
The difference between the two is profound. One supports growth, identity, and self-determination. The other reinforces the long-standing pattern in which disabled people are managed, spoken for, and ultimately viewed as objects of intervention rather than subjects of experience.

